# 🐍 Python Rudiments
batteries included philosophy
- Python Enhancement Proposal - PEP
This is how python language is evolved since 1990.
Python's development is conducted largely through the Python Enhancement Proposal (PEP) process, the primary mechanism for proposing major new features, collecting community input on issues and documenting Python design decisions
# 🛡 General
- immutable basic types (numbers, strings, tuples), are also Primitive types generally
- mutable objects such as lists, dictionaries, and most other types, are generally derieved types
- python REPL interpreter
- callable means which can be called using special method
__call__() - Mixin
- included rather than being inherited
- vue mixins
- Dunder (as in double underscore) /Magic/Special methods in Python
- double underscore methods
- How are dict implemented in python?
- Arguments vs Parameters
- call by assignment
- call by references, howto in python?
- call by value
- Python reads program text as Unicode code points
Python Argument(s) Unpacking
Although, there is no formal rule on calling them *args/**kwargs,
people tend to name them that way. When a function is declared def my_func(*args, **kwargs),
args is a tuple with all positional arguments passed to the function and kwargs is a
with all keyword arguments. They can be named anything as long as the unpack operators * and ** are used.
So * unpacks a tuple and ** unpacks a dict.
- Pickeling/Unpickeling | Marshalling/Unmarshalling | Serialised/Unserialized | jsonify
Pickling is converting an object to a string representation in python. Generally used for caching and transferring objects between hosts/processes.
- Lambda Function
Lambda in Python is an anonymous function created at runtime. E.g.
x = lambda a, b : a * b print(x(5, 6))- Introspection
is the ability to examine an object at runtime.
Python has a
dir()function that supports examining the attributes of an object,type()to check the object type,isinstance(), etc. While introspection is passive examination of the objects,You can instrospect and ask question on objects like?
- tell me how many arguments do you take?
- tell me what code do you contain?
reflection is a more powerful tool where we could modify objects at runtime and access them dynamically. E.g.
setattr()adds or modifies an object's attribute;getattr()gets the value of an attribute of an object. It can even invoke functions dynamically -getattr(my_obj, "my_func_name")()
# 🎏 Data Types
Deals with memory-space management and how garbage collection will work
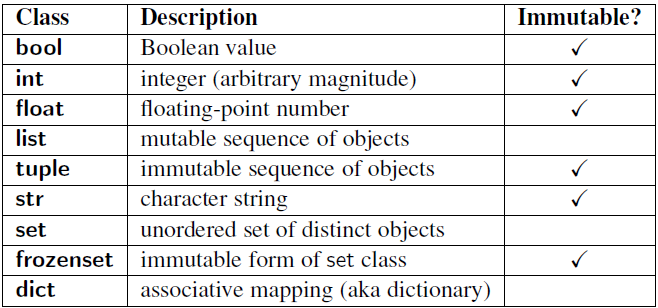
- Python Primitive Data Types
Basic Building blocks
A Byte object is an immutable array
- The items are 8-bit bytes, represented by integers in the range
- Bytes literals (like
b'abc') and the built-inbytes()constructor can be used to create bytes objects. - Also, bytes objects can be decoded to strings via the
decode()method. - create a byte sequence and interprete it as utf-8 string?
str(bytes('XXXX', encoding='utf-8'), encoding='latin-1')latin-1 is 1 ASCII code less than ASCII
- The items are 8-bit bytes, represented by integers in the range
- Python compound / composite Data Structures
built using primitive data types for ease of use in programming
Arrays | Lists | Tuples | Dictionary | Sets | File
open(),readline(),close(),read(),write()- Lists - Linked Lists
Akin to arrays in other languages
- composite / compund data structure
- built using primitive data types
- Slicing operations
- Indexed
- List Manipulation
- List Comprehensions
- composite / compund data structure
- Shallow Copy
shallow copy of the list. Equivalent to
a[:]list.copy()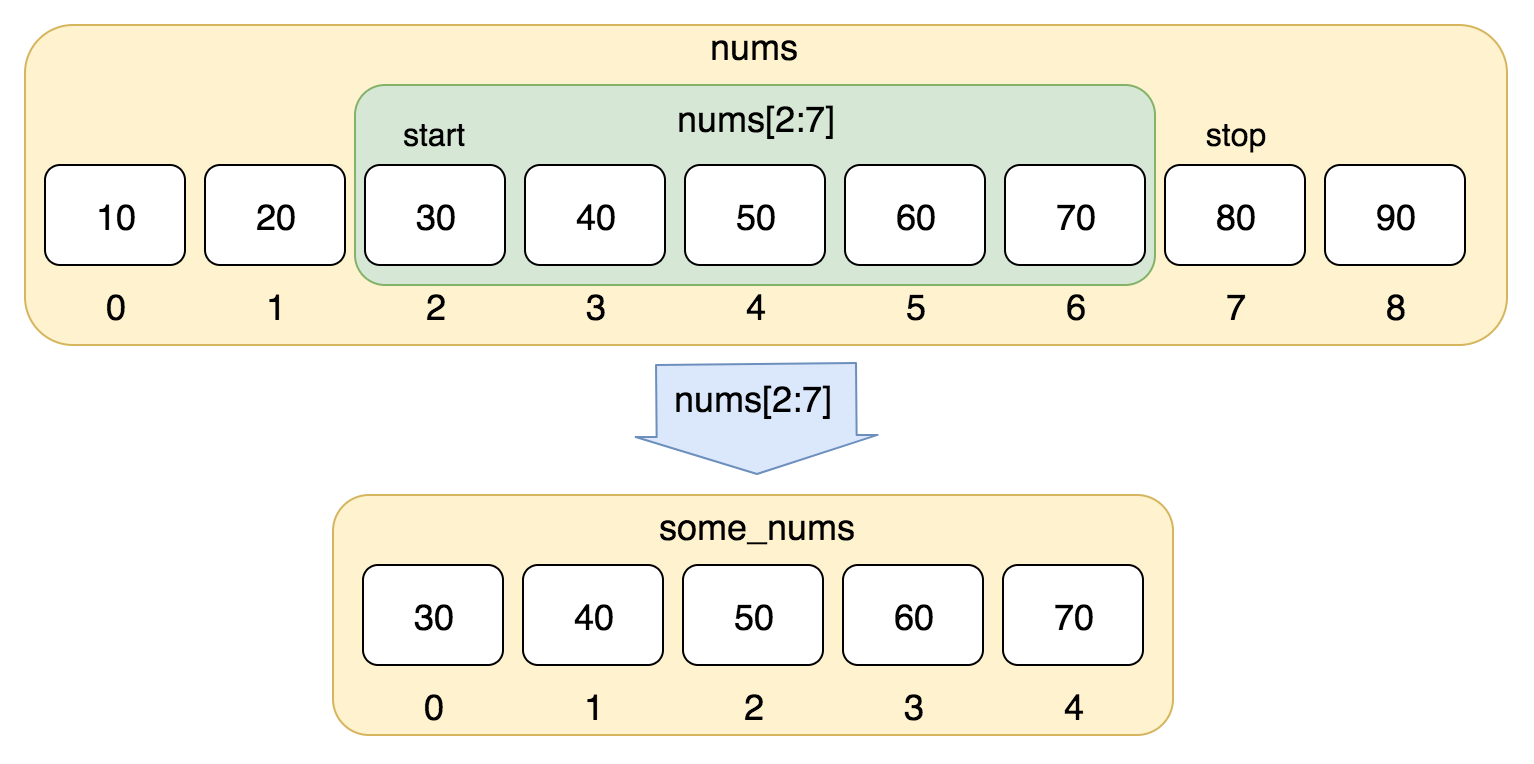
- List comprehensions
creates a new list based on another list, in a single, readable line. aka one-liners
some_list = [1, 2, 'avi', 'mehenwal'] print([ type(item) for item in some_list ])- Dictionaries - Hash Maps
It stores key-value pairs, where keys are unique and it has
access time. The most important limitation for a
dictis that the keys must be hashable/immutable. Meaning, we can use a tuple as a key, but not a list.- Comprehensions in Python
Comprehensions in Python provide us with a short and concise way to construct new sequences (such as lists, set, dictionary etc.)
# 📿 Strings
- C-style string formatting using
%aka old-style - New-style Python
.format()
Since strings are stored as an array of type char in memory, these could be manupulated using
list comprehensions
- Type checking using
isorinstancekeyword
# 📩 Packages and Modules
- Modules for Modular Programming
definitions from a module can be imported into other modules or into the main module
- Executing modules as scripts
- views on using
import *. Are there any dramatic performance changes? - Modules search path
- compiler version of modules saved in
__pycache__directory dir()
- Packages
collection of modules
- structuring python module namespace by using dotted module names
- Packages support one more special attribute,
__path__. This is initialized to be a list containing the name of the directory holding the package’s init.py before the code in that file is executed. __init__.pywill treat the directory it is in as a loadable module.
# 🐌 Exceptions Handling
The try...except statement has an optional else clause, which, when present, must follow all except clauses.
It is useful for code that must be executed if the try clause does not raise an exception.
try:
raise ExcetionName
except ExcetionName:
pass
$ multiple exceptions
else:
# we don't want to catch the ExcetionName exception if it's raised
another_operation_that_can_throw_ioerror()
finally:
print('Runs under all circumstances')
# Else with for loop
def for_else(n):
"""else in for loop is always executed"""
for i in n:
print('Loop', i)
else:
print('Else ', n)# 🏗 Classes
Aliasing
Objects have individuality, and multiple names (in multiple scopes) can be bound to the same object. This is known as aliasing in other languages.
- Class objects support two kinds of operations
- Attribute references and
- Instantiation
- class Attributes
- shared between all instances
- local instances Attributes
- class Methods
- python functions bounded to classname
- Python support Multiple Inheritance
- MRO - Method Resolution Order
- Diamond Relationship Problem
- “Private” instance variables that cannot be accessed except from inside an object don’t exist in Python.
# 🏬 Scopes and Namespaces
- Namespace created by interpreter
is a mapping from names to objects.
Most namespaces are currently implemented as Python dictionaries, but that’s normally not noticeable in any way (except for performance), and it may change in the future. It is like a box where a variable name is mapped to the object placed. Whenever the variable is searched out, this box will be searched, to get corresponding object.
- global namespace at startup
- local namespace when function is called, deleted, exception, modified etc.
- When a class definition is entered, a new namespace is created, and used as the local scope — thus, all assignments to local variables go into this new namespace. In particular, function definitions bind the name of the new function here.
- Scope
is a textual region of a Python program where a namespace is directly accessible. “Directly accessible”
# String formatting
- Old C-sstyled string formatting
- with
.format() - Modern
fstyle strings
name = "Eric"
age = 74
"Hello, %s. You are %s." % (name, age)
"Hello, {1}. You are {0}.".format(age, name)
name = "Eric"
age = 74
f"Hello, {name}. You are {age}."
'Hello, Eric. You are 74.'
# 📕 Standard Library Interfaces
| Function | Library name |
|---|---|
| File System | os, shutil, glob, datetime |
| i/p, o/p, error streams and CLI args | sys |
| Pattern Matching | re |
| Mathematics | math, random, statistics |
| Internet and Web | urllib |
| Data Compression | gzip, bz2 |
| Performance Measurement | timeit, pstats, profile |
| Quality Control | doctest, unittest |
| Threading | multithreading |
# ❓ General Questions
- Modules and Packages
- modules for business logic-BL and module for GUI combined together to form a Packages
- What is the difference between
'and"quotes in python? As far as language syntax is concerned, there is no difference in single or double quoted string.
However, if either single or double quote is a part of the string itself, then the string must be placed in double or single quotes respectively.
str1='Hello "Python"'- Difference between
/,//and%? /classical division return a float//Floor division return an int
# Python reporting, formatted strings
print("{:->20}".format('hello'))
print("{:-<20}".format('hello'))
print("{:->20}".format('hello'))